Key Takeaways
- Ethernet switching is vital for successful network management and performance.
- There are different types of Ethernet switches suited for various networking needs.
- Understanding Ethernet switching can help optimize your organization’s network infrastructure.
Introduction to Ethernet Switching
In today’s digital age, managing network traffic effectively is paramount. As businesses grow and the need for reliable, high-speed connectivity increases, understanding the principles of Ethernet switching can provide a significant competitive edge. But what exactly is Ethernet switching, and how does it impact network performance?
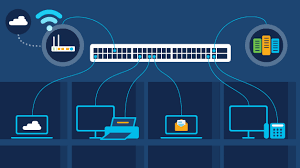
Ethernet switches connect multiple devices within a Local Area Network (LAN). They function like a traffic cop at a busy intersection, directing data to ensure it reaches its intended destination without causing bottlenecks. This becomes increasingly important as the number of devices and volume of data within networks continue to rise. Organizations can use Ethernet switches to enhance their network’s efficiency, reduce latency, and improve overall performance.
What is Ethernet Switching?
Ethernet switching involves directing data packets between devices on a local area network (LAN). Ethernet switches operate at the data link layer of the OSI model, making decisions based on MAC addresses to forward frames to the appropriate destination. The switch maintains a MAC address table that maps devices on the network to specific ports on the switch. When a data frame arrives at the switch, it checks the destination MAC address, looks it up in the MAC address table, and forwards the frame to the correct port. Ethernet switches have emerged as a critical technology ensuring seamless network communication.
This method of packet forwarding helps to minimize collisions and maximize bandwidth utilization. Unlike hubs, which broadcast incoming traffic to all ports, Ethernet switches intelligently route traffic only to the intended recipient. This makes the network more efficient and enhances security by limiting the reach of data traffic to specific devices. Ethernet switches play a pivotal role in maintaining network order and ensuring smooth data flow.
Types of Ethernet Switches
- Unmanaged Switches: Basic plug-and-play devices with no configuration required, ideal for small networks. These user-friendly and cost-effective switches make them perfect for home networks or small offices without advanced features.
- Managed Switches: These offer advanced features such as VLANs, quality of service, and traffic management, suitable for larger, more complex networks. Managed switches can be configured and monitored, allowing network administrators to optimize performance and troubleshoot issues more effectively. Their advanced capabilities make them suitable for enterprise environments requiring high levels of control and security.
- Intelligent Switches: Providing a middle ground, offering some management features while being more user-friendly than fully managed switches. These switches are a good option for growing networks that need some degree of control but only require part of the suite of features found in managed switches. They balance functionality and ease of use, making them ideal for medium-sized businesses.
Benefits of Ethernet Switching
Implementing an Ethernet switch in your network has several advantages, including reduced congestion, improved security, and efficient bandwidth management. Ethernet switches can also prioritize network traffic, ensuring high-priority applications have the necessary resources. This is particularly important for businesses that rely on real-time data transfer, such as VoIP or video conferencing, where delays can significantly impact performance.
Moreover, Ethernet switches are capable of forming virtual LANs (VLANs) for the purpose of dividing network traffic and enhancing security. This division enables sensitive information to be separated from the rest of the network, decreasing the chances of unauthorized entry. Furthermore, Quality of Service (quality of service) features enable network administrators to prioritize critical traffic, ensuring that essential applications receive the bandwidth they need during peak usage times.
Everyday Use Cases for Ethernet Switching
Ethernet switches are integral to various applications, from small office setups to large enterprise networks. For instance, businesses using VoIP systems rely on Ethernet switches for low-latency communication. The switch’s ability to prioritize voice traffic ensures clear, uninterrupted calls, essential for professional communication.
Similarly, organizations with multiple connected devices leverage switches to maintain high-speed data transfer and connectivity. Ethernet switches facilitate seamless access to digital resources and online learning platforms in educational institutions. Retail environments use switches to support point-of-sale systems, inventory management, and surveillance systems. The versatility of Ethernet switches makes them essential components in any modern network infrastructure.
Ethernet Switching in Data Centers
Ethernet switching is critical in handling massive data traffic in data centers. High-density switches connect servers and storage systems, providing a robust infrastructure for virtualized environments and cloud services. This connectivity ensures that data can be quickly and efficiently moved between devices, supporting data processing and storage demands.
Data centers require switches with high port density, low latency, and advanced traffic management features. These switches must handle large volumes of traffic while maintaining optimal performance. Managing and configuring these switches remotely is also crucial, as it allows data center administrators to monitor performance, identify issues, and make adjustments without physical access to the hardware. With the rise of cloud computing and big data, the importance of reliable and efficient Ethernet switching in data centers cannot be overstated.
Future Trends in Ethernet Switching
The landscape of Ethernet switching is continuously evolving. Emerging trends, such as integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning for automated network management, are set to revolutionize the industry. These technologies enable switches to analyze traffic patterns, predict potential issues, and adjust configurations automatically to optimize performance and security.
Furthermore, advancements in Ethernet technologies like 400G and beyond promise to further enhance network speeds and efficiency. These high-speed connections support the growing demands of data-intensive applications such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and high-definition streaming. As networks expand and evolve, Ethernet switching technology will ensure they remain fast, reliable, and secure.
Recent reports highlight that Ethernet technology is becoming increasingly vital as organizations seek to upgrade their infrastructure to handle more data with higher reliability. This trend underscores the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in Ethernet switching technology to ensure your network can meet future demands.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of Ethernet switching in today’s network infrastructure is paramount for any organization looking to enhance its network performance. By choosing the right type of switch and staying informed about industry trends, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and ensure efficient and secure communication across their networks.
Reputable sources such as TechRepublic provide comprehensive analyses and updates for those interested in more in-depth insights into Ethernet switching technologies. By leveraging the knowledge and expertise available through these resources, you can better navigate the complexities of network management and optimization, ensuring that your organization remains competitive in an increasingly connected world.